

SOLUTIONS
ENERGY HIERARCHY
The Energy Hierarchy is a classification of energy options, ordered to assist in attaining a sustainable energy system. The conservation of energy and energy efficiency is the highest priority. The production of sustainable energy is the next priority while waste-producing energy generation is the lowest priority.
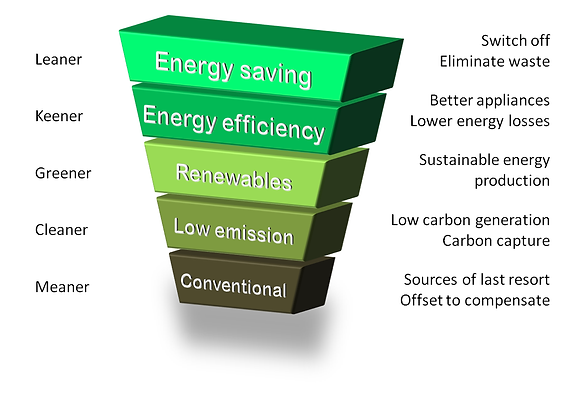
ENERGY SAVING
The top priority in the Energy Hierarchy. Energy conservation is the process of reducing energy consumption, restricting the unnecessary use of energy, and eliminating waste.
Energy conservation includes turning off unused lights, unplugging unused appliances, avoiding unnecessary travel, and insulation of heat inside structures. Conservation of energy can help increase environmental quality, national security, and personal financial security.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY
The second priority in the hierarchy to ensure that energy is used efficiently. Energy efficiency has two main parts: conversion efficiency of energy consumption and conversion efficiency of energy production.
Conversion Efficiency of Energy Consumption or efficient energy use is the goal of reducing the energy required to provide products and services.
Conversion Efficiency of Energy Production is the goal of reducing the losses in energy production and improving the efficiency of energy conversion.
RENEWABLES
Renewable energy is the energy that is produced using renewable sources, an energy resource that is treated as infinite and replenish within a human's lifespan. Renewable energy falls under two categories: elemental and bio-energy.
Elemental renewables are energy derived from climatic or elemental sources such as sunlight, wind, waves, tides, and heat of the Earth.
Bio-energy is energy derived from biomass. The short growth cycle means that usage of biomass is immediately replenished. Bioenergy is created by combustion and emits carbon into the atmosphere which is then absorbed by the plants during the growth cycle.
LOW EMISSIONS
Low impact energy production is the fourth priority in the Energy Hierarchy. These are energy produced from sources that are not fully sustainable but have a low impact on the environment.
Low impact energy production includes the burning of fossil fuel with carbon capture and storage (CSS). Nuclear energy is sometimes treated as a low impact source because of its low carbon emissions.
CONVENTIONAL
High-impact energy production has the lowest priority in the hierarchy. Conventional energy is the production of energy using sources that are unsustainable and has a high impact on the environment. Nuclear energy is sometimes placed in this category because of its hazardous waste and depletion of uranium.
Switching from high damaging fuel sources (such as coal) to less damaging sources (such as natural gas) can limit the adverse effects.
When the usage of high-impact energy is reduced, the effects of any residual should be balanced through carbon offset.
